Explore Qwen3
Investigate a feature-level “brain scan” of Qwen3 with cross-layer transcoders and topological coactivation maps revealing how the model transforms information.
Learn how it works
TRUSTED BY
Visualize
the entire model.
See inside Qwen3’s multi-layered mind, with interactive topology to guide you, powered by BluelightAI’s Cobalt.
Interpret
feature activations.
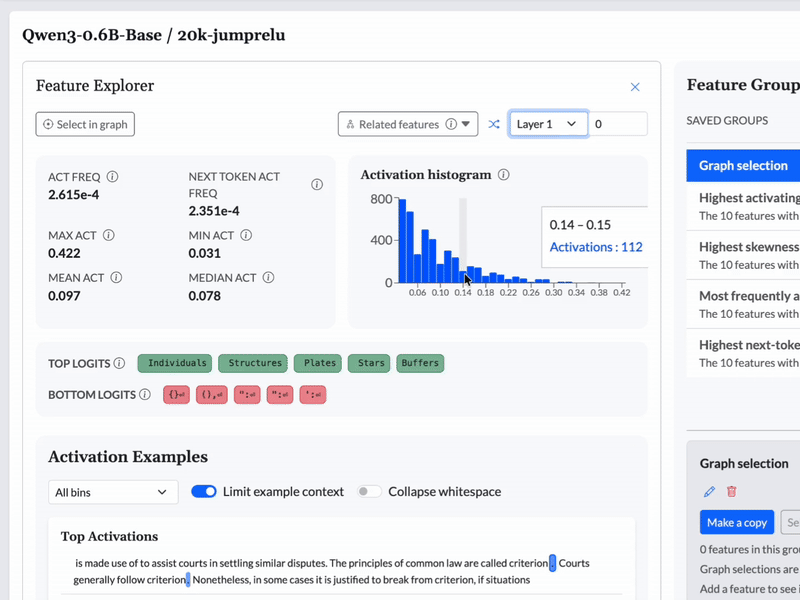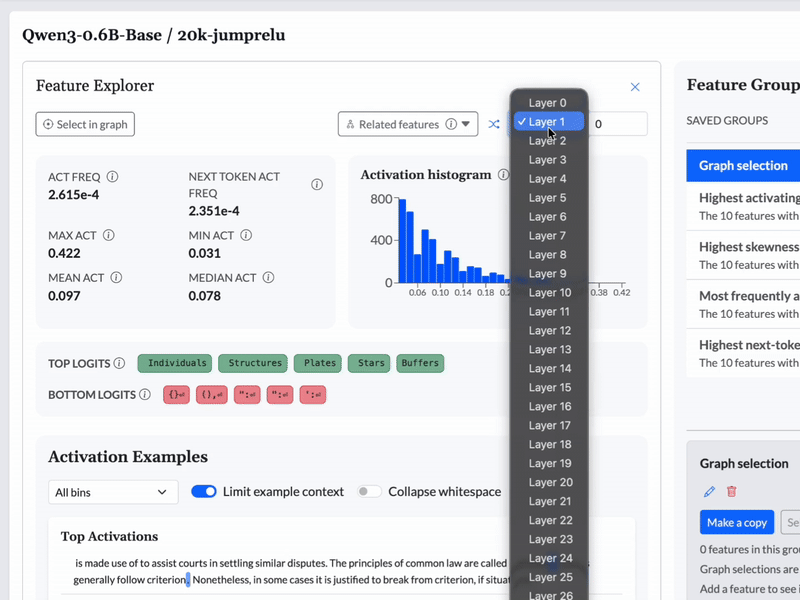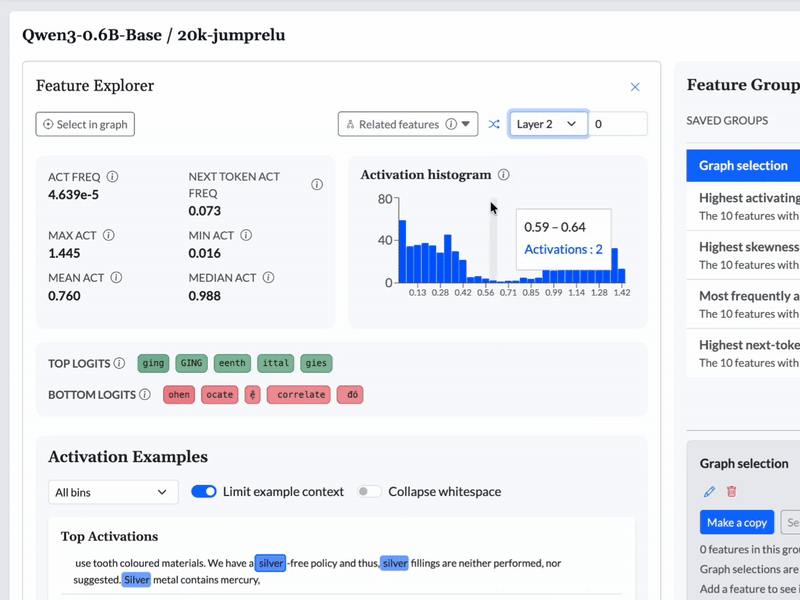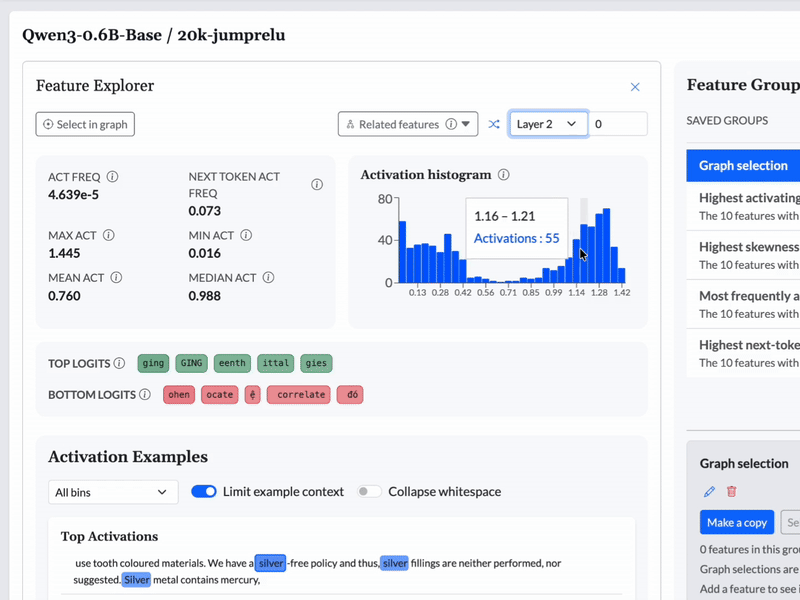
See which features light up when queries are made. Identify patterns in how the model processes information.
Understand
model internals.
Our mission is to illuminate the shadowy internals of AI systems so you can understand what’s really going on.
FAQs
-
BluelightAI trained cross layer transcoders for Qwen3-0.6B Base and 1.7B Base to let anyone explore the internal workings of one of the most capable open source AI models being used today.
-
Cross-layer transcoders (CLTs) are AI models trained to interpret another AI model. They break down the input of each layer of the source model into combinations of interpretable features, and use those features to reconstruct the output of that layer and subsequent layers. This helps explain the work that each layer performs in terms of human-interpretable concepts.
CLTs were developed by researchers at Anthropic to make discoveries about how LLMs perform tasks, and recently open source CLTs have been released for Gemma 2 and Llama 3.2. However, no CLTs have been available for the Qwen3 models, which are among the most popular open-weights models today. We're fixing that problem with these Qwen3 CLTs.
-
We can use a CLT to give an LLM a "brain scan" as it processes an input, and identify which features are activated—in other words, what the model is thinking about. In some scenarios, knowing the features that are active can be enough to let you predict what the model will or should do.
We can go even deeper, though. Researchers have used CLTs to build attribution graphs for prompts, which trace the model's computation through individual features to understand the factors that influence its output. This can produce very detailed explanations of how a model is able to perform a particular task.
-
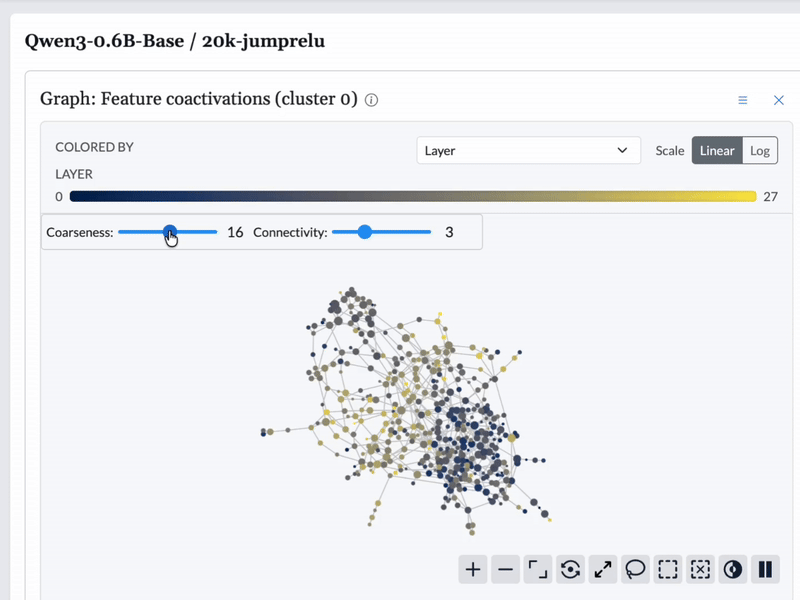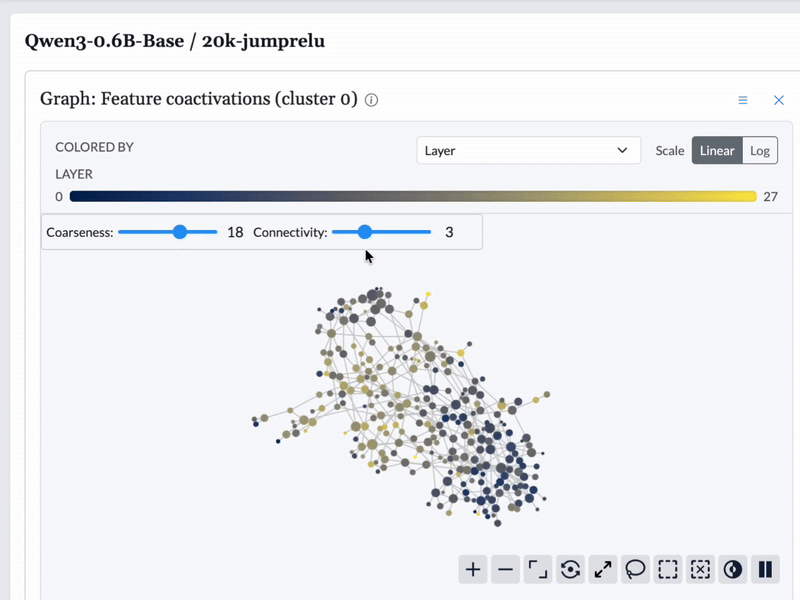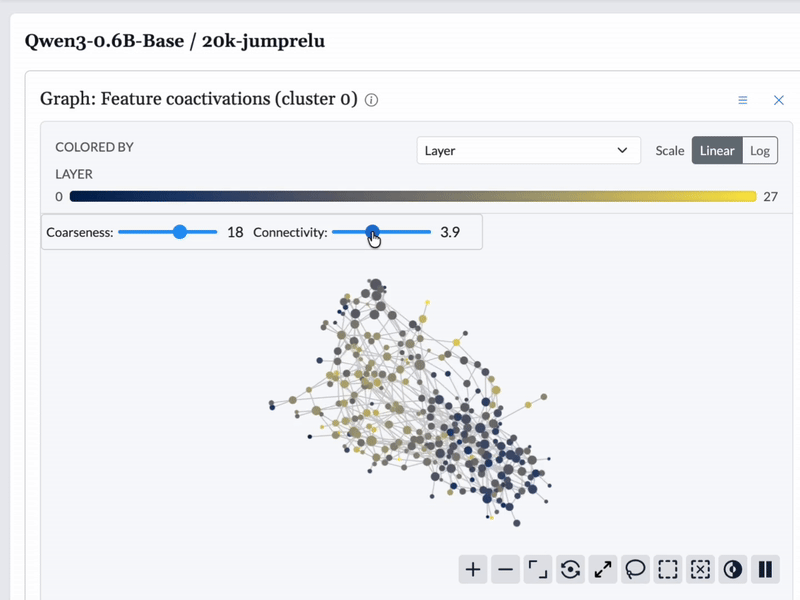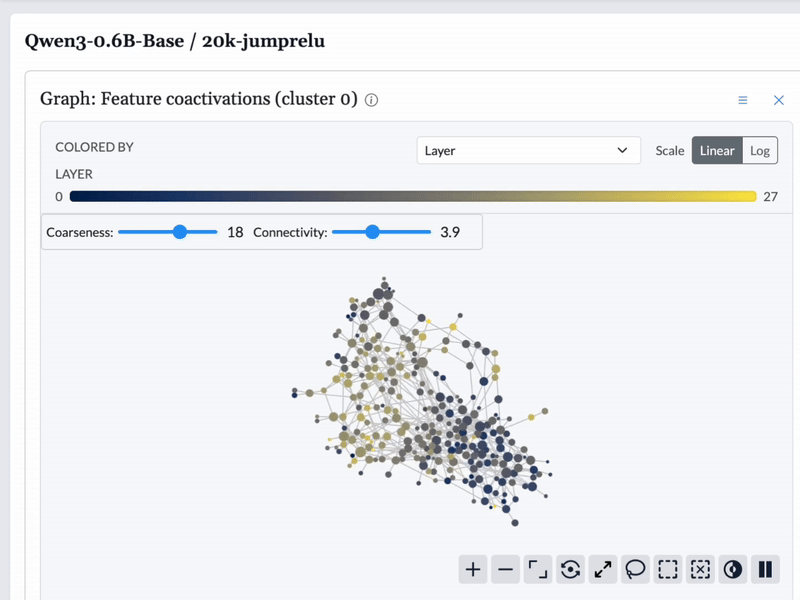
We used Cobalt to construct topological graphs from the features from each model. These graphs are multiresolution representations of the set of features, displaying groups of related features as nodes with connections between them. These graphs are available to browse in the feature dashboard.
Graphs are built based on different similarity measures for each feature. We built graphs based on feature encoder vectors, feature decoder vectors, and feature coactivation patterns. For encoder and decoder vectors, we built one graph for each layer, as it is not immediately obvious that feature vectors from different layers are comparable.
“Data has shape, and the shape matters.”
– Gunnar Carlsson, Cofounder & CTO of BluelightAI
Dive deeper
Contact Us
Interesting in building with Cobalt?